-
Apps
How to Use Instagram? In Depth Pathway!
Are you looking to harness the power of social media to connect with friends, explore interests, or even promote your…
Read More » -
Computer
What is SSD or Solid-State Drives? A Comprehensive Guide!
Throughout extensive research and analysis from various online sources, including articles, online communities, and personal experiences, I have delved into…
Read More » -
Computer
What Are Printers? Know the Types and their Working! A brief Guide!
In my early life, I had the opportunity to work as a computer operator, where I had the chance to…
Read More » -
Computer
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Perfect Computer Keyboard
Get ready to revolutionize your digital experience with the ultimate guide to choosing the perfect computer keyboard. Whether you’re seeking…
Read More » -
Computer
What is a Computer Mouse and Parts of a Mouse and its Functions!
A computer mouse is an important device that helps us interact with computers. It allows us to control a small…
Read More » -
Computer
Elevate Your Visual Experience: The Ultimate Guide to Monitors and VDUs
In the digital age, captivating visuals are crucial for work, entertainment, and communication. Monitors and VDUs shape how we perceive…
Read More » -
Computer
A Comprehensive Guide to ROM: Types and Their Applications
In the fast-paced world of Information Technology (IT), where digital innovations shape our daily lives, understanding the underlying technologies becomes…
Read More » -
Computer
Inside the World of Graphics Cards: A complete guide How GPU works?
Get ready to delve into the captivating world of graphics cards and discover how they play a vital role in…
Read More » -
Computer
What is RAM? Exploring the Basics of Random Access Memory
RAM, the cornerstone of computer memory, powers our digital experiences. It fuels applications, empowers multitasking, and ensures smooth execution. RAM…
Read More » -
Internet
Project Gutenberg – Everything you Want to Know!
Project Gutenberg library offers you 60,000+ free eBooks — nowhere close to other libraries, right? Well, there’s a good reason…
Read More » -
Internet
PDF Drive Website – Everything You Want to Know
It’s a Z-library competitor website, which is quite popular as well. Reportedly, PDF Drive offers you around 78 million free…
Read More » -
Computer
The Basics of a Computer Processor: What it is and How it Works?
As per my experience, understanding the basics of a computer processor is crucial for anyone seeking to dive into the…
Read More » -
Computer
What is a Motherboard in a Computer? Exploring the Heart of a Computer!
The motherboard is a crucial component that serves as the heart of a computer system. It plays a vital role…
Read More » -
Internet
Archive.org Open Library – A Complete Guide
Archive.org / Open Library is one best alternatives to Z-Library which provides you with millions of free eBooks, millions of…
Read More » -
Internet
PDF Magazines – Everything you Want to Know
PDF Magazines are for downloading magazines, instead of eBooks and articles. There are over 6000,000+ magazines, including the latest releases.…
Read More » -
Internet
EPDF – An Excellent eBook Resource for Free!
EPDF is another excellent free resource for downloading eBooks. It only gives you books in PDF format so you don’t…
Read More » -
Computer
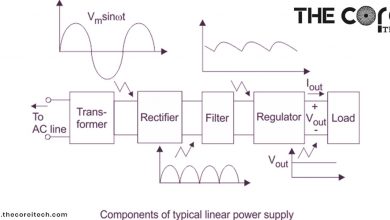
How Does a Regulated Power Supply Work?
Advantages of Regulated Power Supply: A regulated power supply is an electronic device that regulates the voltage and current supplied…
Read More » -
Computer
Important Power Supply Form Factors Explained!
Power supply form factors are the dimensions, shapes and other physical specifications of power supplies. These specifications define how a…
Read More » -
Apps
What is Picuki? Discover Everything You Need to Know
In the age of social media dominance, platforms like Instagram have revolutionized the way we connect, share, and discover content.…
Read More » -
Computer
What Is a Power Supply and How Does It Work?
Today I am going to share my finding and understanding about a most important component of a computer which you…
Read More » -
Apps
Truth Social App: The Twitter, Trump, and Musk Controversy
Donald Trump, the former US president, has launched Truth Social, a new social media platform that aims to provide an…
Read More » -
Computer
What Is a Hard Disk Drive (HDD)? A Comprehensive Exploration
A Hard Disk Drive (HDD) is a fundamental component of modern computer systems, serving as a primary storage device for…
Read More » -
Technology
How many types of drones are there? – Explore the UAV’s
In the exciting world of technology, drones have become incredibly popular and useful. These unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are everywhere,…
Read More » -
Internet
Discovering the World of Books: Z-Library
In a world filled with endless possibilities, there are few treasures as captivating as a good book. For someone like…
Read More » -
Computer
What are the standard laptop sizes?
Everyone has different choices and personal preferences in standard laptop sizes and laptop dimensions. You should choose the technology which…
Read More » -
Reviews
Best Pc for Streaming Review
Building a PC for streaming from scratch sucks! You’ve to go through countless intimidating callings such as buying the right…
Read More » -
Reviews
Best RGB RAM to Buy? My Personal Review!
Want that extra glare in your PC setup? I mean, why not let the RAM shine, when the other parts…
Read More » -
Reviews
Best Wireless Display Adapter Review — Go Truly Wireless
Are you someone who hates messy, tangly wires? I mean you’re someone who loves a clear, crisp, and high-quality display…
Read More » -
Computer
Top Fastest Operating Systems
If you looking for information about Best OS for PC, you are in right place, because I am going to…
Read More »